
Honeysuckle flowers are the dried buds or blooming flower of Lonicera japonica Thumb, where the main effective component in the stems, leaves and flowers is chlorogenic acid (CGA) that is present as brown powder. CGA displays extensive pharmacological effects that are primarily manifested in anti-inflammatory and antibacterial aspects, and has a certain effect for the treatment of influenza and inflammation. CGA is widely used in medicine, daily chemical industry, health care products, food and other fields.
Structure
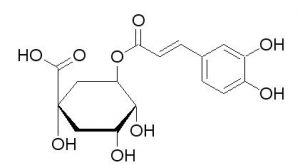 CGA, also known as coffee tannic acid, is a condensation product of caffeic acid and quinic acid. It is also a kind of phenylpropanoid compound produced by plant through oxalic acid pathway during aerobic respiration. Theoretically, there are 10 kinds of CAG isomers composed of mono-quinylquinic acid and dicaffeoyl quinic acid based on the difference between the number of binding sites and the number of caffeoyl on quinic acid.
CGA, also known as coffee tannic acid, is a condensation product of caffeic acid and quinic acid. It is also a kind of phenylpropanoid compound produced by plant through oxalic acid pathway during aerobic respiration. Theoretically, there are 10 kinds of CAG isomers composed of mono-quinylquinic acid and dicaffeoyl quinic acid based on the difference between the number of binding sites and the number of caffeoyl on quinic acid.
Physicochemical Properties
Semi-hydrate of CGA is present in a form of white or yellowish acicular crystal, and becomes anhydrous at 110 °C. It is easy to dissolve in polar solvents such as ethanol, acetone and methanol, but difficult to dissolve in the lipophilic organic solvents, such as trichloromethane, ether and benzene. CGA as an ester formed by caffeic acid and quinic acid contains ester bond, unsaturated double bond and polyphenol, Herein, in the process of plant extraction, isomerization is often caused by hydrolysis and migration of lactone groups. It can be isolated from plants using ethanol, acetone, methanol and other polar solvents, while the extraction of CGA can’t be heated at high temperature and strong light for long time because of the instability of CGA.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
The oral absorption of CGA is poor with only a small fraction being absorbed the small intestine in a prototype, and most of them enter the colon and are metabolized by microbial into substances like benzoin, phenylpropionic acid and cinnamic acid to be absorbed. Therefore, after oral administration of CGA, it mainly appears as metabolite in plasma. Antibiotics can affect the normal microbiota of colon, thus affecting the intestinal metabolites concentration of CGA in the plasma. CGA could bind with human serum albumin (HSA), and the mode of binding varies in different concentrations. The metabolism of CGA might associate with P450 enzyme. CGA and its metabolites in plasma are excreted mainly through the kidneys.
With the deepening of research on CGA, a more comprehensive understanding of CGA has been explained and provides an important theoretical basis for the scientific pharmacy and rational drug use. The bioavailability of oral CGA is low and depends on the activity of colonic microorganisms. Therefore, intravascular administration is the best way to fully exert the efficacy of CGA, and the effect of oral administration of CGA may be directly caused by its metabolites.
Pharmaceutical Effects
CGA exhibits activities against bacteria and could enhance the immune function of human body. It inhibits protein synthesis of drug-resistant bacteria and has a significant stimulating effect on the respiration of Staphylococcus aureus resistant plants. It has been exploited for the control of internal and external inflammation caused by drug resistant strains. It is also helpful to reduce the rate of laryngology. Pharmaceutical efficacies of CGA include protective effect of cardiovascular, anti-mutagenesis and anticancer effect, lipid-lowering effect, anti-leukemic effect, immunomodulatory effect, hypoglycemic effect and so on. CGA also blocks the formation of cytokines and chemokines caused by staphylococcal exotoxin, and inhibits the contraction of fibroblast collagen net frame caused by hypertrophic scar-derived fibroblasts (mFs) and the increase of the suprarenal cortical hormone (ACm) induced by stress response.
As mentioned above, antibiotics can affect the absorption of CGA in the gastrointestinal tract. It is also reported that the excretion of CGA (one of the effective components in Shuanghuanglian) and antibiotics may be reduced when Shuanghuanglian and antibiotics are administered intravenously. This mechanism may be related to the competitive excretory channel. CGA can also restrain the absorption of iron and dietary non-heme iron, and promote the absorption of aluminum ions. In vitro studies have shown that CGA can inhibit the activity of P4502B1 in the rat liver and affect the metabolism of its substrate of coumarin derivatives.
In pharmacodynamics, the newly discovered CGA has a significant pharmacological activity, which gives new inspirations for the development of new drugs. Due to the interaction of drugs, the clinical combination of drug use should be paid attention. The efficacy of the interaction between CGA and antibiotic depends on the way of giving CGA. To sum up, the widely distributed CGA has a variety of pharmacological effects and thereby the acceleration of the investigation and development of CGA is of great significance.

Leave a Reply